Deira - Dubai
Products & Services:
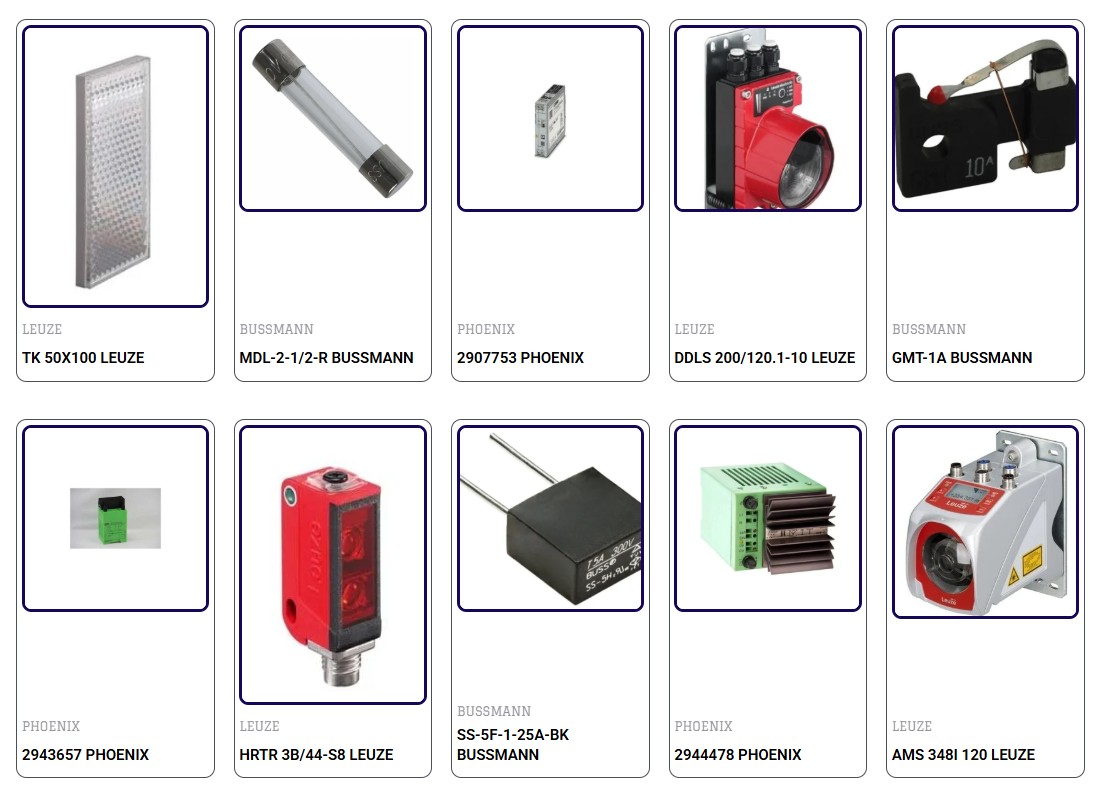
Supplier of GARMIN Watches, MENNEKES Electrical Equipment and Supplies, SUNLIGHT BATTERY Battery, YU More..
Supplier of GARMIN Watches, MENNEKES Electrical Equipment and Supplies, SUNLIGHT BATTERY Battery, YUVIX Electrical Equipment and Supplies, 3M Electrical Equipment and Supplies, AAEON Computer Systems and Software, AAG STUCCHI Electrical Switchgear, ABB Switches and Sockets, ABRACON Generators, ABSOPULSE Uninterrupted Power Supply, ABTECH Electrical Equipment and Supplies, ACDC Electric Fans, ADAFRUIT Electrical Switchgear, ADEL SYSTEM Power Supply, ADOS Gas Detectors, AGILE EUROPE Battery, AIM-TTI Electrical Switchgear, ALLEN BRADLEY Industrial Automation, ALLIED SAFETY SHOES Safety Equipment and Clothing, ALPS ALPINE Switches and Sockets, AMARON Battery, AMPHENOL Industrial Automation, ANALOG DEVICES Amplifiers, ANAMET EUROPE Conduit and Conduit Fittings, ANCHOR Electrical Equipment and Supplies, ANOLIS Lighting Fixtures, ARDUINO Switches and Sockets, ARMAC MARTIN Electrical Sockets, ARRESTEK Earthing and Lightning Protection, ASSMANN Cable and Wires, ATKORE Conduit and Conduit Fittings, AUER SIGNAL Switches and Sockets, AUTOOL Measuring and Testing Instruments, BELIMO Valves, BENDER Transformers, BENEDICT Electrical Switches, BEST Heating Systems, BG Switches and Sockets, BI TECHNOLOGIES Industrial Automation, BIFOLD Fluid Control Systems, BIHL+WEIDEMANN Industrial Automation, BIVAR Industrial Automation, BLAZE Sensors, BONING Industrial Automation, BRAINBOX Industrial Automation, BREMAS Switches and Sockets, BRIDGETEK Sensors, BRIGHTEK LED Light Sensors, BROADCOM Industrial Automation, BROYCE Electrical Equipment and Supplies, BTS Electrical Switches, BULGIN Electrical Equipment and Supplies, BURKERT Valves, C&K Switches and Sockets, CAL Electrical Equipment and Supplies, CAMSCO Electrical Equipment and Supplies, CANFORD Sensors, CAPRONI Solenoid Valves, CASAMBI Electrical Equipment and Supplies, CDC Valves, CDIL Industrial Automation, CE+T POWER Uninterrupted Power Supply, CELLPACK Cable Accessories, CEMBRE Cable Accessories, CFRIEND Fuses, CHARNAUD Safety Wear, CHERNE Pneumatic Equipment, CLEON Battery, CLEVER LIGHT Electrical Equipment and Supplies, COMELETRIC Switches and Sockets, CONTA CLIP Electrical Equipment and Supplies, CONTACTUM Industrial Automation, CRE CONTROLLER Electrical Equipment and Supplies, DATASENSOR Sensors, DESCO Electrical Equipment and Supplies, DF ELECTRIC Electrical Equipment and Supplies, DFROBOT Industrial Automation, DIELL Sensors, DISPLAY TECHNOLOGIES Electrical Equipment and Supplies, DIVEVOLK Industrial Automation, DNE Cable and Wires, DNE CAVI Flexible Cables, DOLPHIN Battery, DOTZAUER Flexible Cables, DRUCK Sensors, DUCATI Electrical Equipment and Supplies, DURA SAFE Safety Shoes, DURACELL Battery, EAO Electrical Switches, EASE Cable Accessories, EDMI Industrial Automation, ELEKTRA EFFLUX Cable Accessories, ELERON Switches and Sockets, ELFIN Cable Accessories, ELKO EP Industrial Automation, EMAS Electrical Equipment and Supplies, ENERGYCELL Battery, ENKO ELECTRONICS Battery, ENOVATIONCONTROLS Pressure Gauges, ENTRELEC Cable Accessories, ERA Electric Fans, ESBEE Industrial Automation, ETA ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGIES Industrial Automation, ETI Industrial Automation, EUROPA COMPONENTS Switches and Sockets, EVEREADY BATTERY Battery, EVERSPIN Electrical Switches, FABERGE LED Lights, FABLER Flood Lights, FASCO MOTORS Motors, FEBERG Flood Lights, FIBOX Enclosures, FISCHER ELEKTRONIK Electrical Equipment and Supplies, FLUKE Measuring and Testing Instruments, FUJI Electrical Switchgear, FUSELEC Fuses, GEFRAN Industrial Automation, GK BATTERY Battery, GLOBAL Battery, GM INTERNATIONAL Battery, GREATWHITE Electrical Equipment and Supplies, GREENLINE Tools, HABOTEST Measuring and Testing Instruments, HELUCABLE Cable Accessories, HENGSTLER Industrial Automation, HENZA Electrical Equipment and Supplies, HIKMICRO Measuring and Testing Instruments, HIKVISION Security Control Equipment, HINODE FUSE Industrial Automation, HIQUEL ELECTRONICS Industrial Automation, HOHNER Industrial Automation, HONEYWELL Safety Equipment and Clothing, HT Measuring and Testing Instruments, HUBBELL Switches and Sockets, HVI Measuring and Testing Instruments, HY-LOK Valves, HYDAC SENSOR Sensors, IBERLAMP LED Lights, ICOTEC Cable Gland and Lugs, IDEAL Cable Accessories, IGUS Cable Accessories, IME Battery, IMO Actuators, IMPRESS Sensors, INVEREX Inverters, IORNCLAD PERFORMANCEWEAR Safety Equipment and Clothing, ISKRA Electrical Equipment and Supplies, ITALWEBER Transformers, ITOOLS Tools, JST Electrical Equipment and Supplies, KANDOLIT LED Lights, KEMET Electrical Equipment and Supplies, KHAITAN Electric Fans, KINGTONY Tools, KLAUKE Hand Tools, KLOEHN Valves, KUDOS Industrial Automation, LAWSON Fuses, LAYTRON LED Lights, LECXO Battery, LEDIL Electrical Equipment and Supplies, LEMO Cable Accessories, LINDNER FUSE Fuses, LINDSTRÖM Hand Tools, LITEON Industrial Automation, LITHIUM POWER Battery, LITTELFUSE Electrical Equipment and Supplies, LUMEL Measuring and Testing Instruments, LUMINOUS Battery, LUXE LED Lights, MAXAIR Industrial Automation, MAXLITE Lighting Fixtures, MEM Electrical Switchgear, MENNEKES Switches and Sockets, MERLINGERIN Electrical Switchgear, MICOLUX LIGHTING Lighting Fixtures, MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC Electrical Switchgear, MOXA Industrial Automation, MUST Industrial Automation, NOV BATTERY Battery, OKAYA BATTERY Battery, OMRON Industrial Automation, OSRAM Industrial Automation, PANDUIT Cable Ties, PILZ Industrial Automation, PRYSMIAN Cable Accessories, PULS Power Supply, RAYCHEM Electrical Equipment and Supplies, RITTAL Electrical Equipment and Supplies, SAFT Battery, SCHNEIDER Electrical Equipment and Supplies, SIEMENS Industrial Automation, WAGO Industrial Automation, YUASA Battery, ZAMEL Industrial Automation, ZIEHL Industrial Automation in Dubai, UAE. Less..
Since : 2022